COVID-19
Health resources, information, and advice to protect yourself, your family, and your community.
With the normalization of COVID-19 the following health advice is recommended if you test positive for COVID-19:
- It is highly encouraged that you self-isolate for up to 7 days:
- You can exercise at your own time, however do not go to public places i.e. gyms, indoor facilities or other areas where groups of people will be
- If you are to leave your residence we do ask that you wear a mask and do not gather with other people.
- Those living with you do not have to quarantine but if they do start to have symptoms then to conduct a test and if positive then to self-isolate as well.
- If you are not symptomatic (please click on link for list of symptoms Click Here) then after 3-5 days you can leave your residence and carry on as per normal. You do not require a health officer to provide a formal release
- Should you require a medical certificate/sick leave or medical care please call your local health facility. TMO Health Facilities
- If you have conducted a Rapid Antigen Test (RAT) please report your positive test result to your local health facility or on Te Marae Ora’s online reporting form Positive COVID-19 Form
The above also apply to visitors who may test positive for COVID-19 while on holiday here in the Cook Islands. Continual health support from Te Marae Ora is accessible through Tupapa Primary Healthcare on 20066, after hours at the Rarotonga Hospital on 22664 or the Health Intelligence Unit on 56180.
COVID-19 Testing
Where to get a COVID-19 test
It is encouraged that you take a COVID-19 test if you have cold, flu or COVID-19 symptoms or are a close contact of a positive case. Testing locations can be found below:
- Village Clinics/Punas (Mon – Thurs 8am – 3pm, Fri 8am – 1pm)
- Tupapa Primary Health Care (At your expense. Please call first and book an appointment)
- Aitutaki Hospital (Please call first)
- Pa Enua Health Facilities (Please call first.)
Learn more about the types of COVID-19 tests here. View the locations of your village Clinic/Puna and Health centres here.
Conducting an RAT test for your Business or home?
If you are a Health and Safety Officer for your business or are conducting personal RAT tests at home, please record all tests using these forms below.
- RAT Testing Summary Form – This form is used to record the daily RAT tests conducted at each location/organization/personal
- RAT Test Positive Case Form – This form is used to record up to 10 positive cases. If there are more than 10 cases in any given period, users will be required to fill this form twice.
Cook Islands COVID-19 Case Statistics
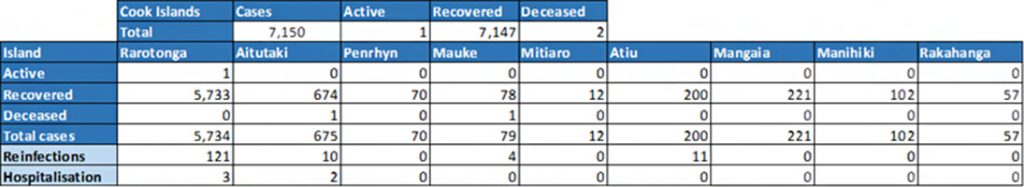
Statistics retrieved 10 May 2023.
Public Health Measures
COVID-19 mainly spreads from person-to-person through infected droplets released when a sick person sneezes or coughs nearby another person’s mouth and nose. Te Marae Ora recommends these simple steps to keep yourself and your families safe.
10 Public Health Tips to Keep You Safe
- Wash your hands with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitiser
- Practise pragmatic physical distancing (at least 1m)
- Cover your coughs and sneezes
- Avoid touching your face (eyes, mouth, nose) with unwashed hands
- Stay home when unwell
- Wear a face mask if unwell, in public, crowded, or enclosed spaces
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces
- Limit time spent in crowded and enclosed spaces
- Protect vulnerable people in our community
- Avoid spreading misinformation
Vaccination
Te Marae Ora (TMO) and the Government of the Cook Islands aims to get all eligible Cook Island residents vaccinated. The vaccine will be free to Cook Islands residents only. The COVID-19 vaccination will be free of charge and completely voluntary.
What vaccines will be available
COVID-19 vaccines that is made available to the Cook Islands is Pfizer. More information on the vaccine can be found below:
Who can get a vaccine?
You can get a free vaccine if you are a resident of the Cook Islands or hold a work permit to work here. The vaccine is available and recommended to persons +12 years of age. The vaccine is also recommended for persons from 5 to 11 years of age but a consent form is required from the parents or caregivers of the child. Please note that the dosage of Pfizer vaccine is different from the dosage given to those aged +12 years old. Any information collected will not be used for immigration purposes. We are expecting enough vaccines for the rest of the eligible people of the Cook Islands. The vaccine is not recommended for people under the age of 5 years or have a history of severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine and they should not take it.
Should pregnant women be vaccinated?
While pregnancy puts women at higher risk of severe COVID-19, very little data is available to assess vaccine safety during pregnancy. Pregnant women may receive the vaccine if the benefit of vaccinating a pregnant woman outweighs the potential vaccine risks. For this reason, pregnant women at high risk of exposure to COVID-19 (example health workers) or who have comorbidities, which add to their risk of severe disease, may be vaccinated in consultation with their health care provider.
When will you get the vaccine
The COVID-19 vaccine will be rolled out through a COVID-19 Immunisation programme as supply becomes available. Rollout dates are identified but may change depending on when the vaccines arrive and what’s happening in our community, NZ and the region.
Vaccination Stations location
The vaccines will be given to the general public at Rarotonga Hospital. The vaccination sites in the Pa Ena will be located at the TMO hospitals or clinics. TMO will confirm if any changes to venues and will issue vaccination times and groups closer to the dates.
Medical exemption for vaccine
Those who are not able to receive a COVID-19 vaccine due to medical reasons must be exempted. To apply for an exemption you must fill out a Medical Exemption application, and email the completed application to covidvacmedexemption@cookislands.gov.ck . Your application will be processed within 10 working days.

Book an appointment - Pfizer vaccination
Make an online booking to have your vaccine shot. Click here to make appointment – covid-19 vaccination appointment
Digital Vaccination Certificate
What is a Digital Covid- 19 Vaccination Certificate?
It is valid digital document that serves as proof that you have been fully vaccinated. To ensure all persons whom have been vaccinated can provide a valid form of proof digitally. This can only be done via a Digital Vaccination Certificate that can be stored/saved on any of your devices electronically.
In order for the Digital Vaccination Certificate to be valid and verified against your Bio data – the records must match either your Passport Name and/or your Birth Certificate.
Events and Gatherings
View updated Ministerial order concerning private and public events gathering and what restrictions. Here.
1. All indoor and outdoor events and social gatherings, whether in a private or public setting, organised or spontaneous, are restricted to a specific number of people dependent on the Island you live on, unless an exemption has been obtained from the Secretary of Health (or delegate).
2. This includes (but is not limited to) parties; fundraisers; team sports training and games; sporting events; funerals; weddings; live shows; the cinema; night clubs and family land meetings.
3. This does not include a gathering for the purpose of business or service –
- at an office or workplace; or
- as part of ordinary retail operations; or
- at a hearing of a court or tribunal; or
- churches, cafes, restaurants and bars; or
- as part of ordinary operations at an education entity.
Contact Sports
4. All forms of contact sports, whether in a public or private setting, are prohibited, including training and match play.
Contact sports means any sport that involves the participants coming into bodily contact with one another as an accepted part of play.
What defines a Gathering?
Gatherings are situations where people are intermingling in a group and remain closer than 2 metres from each other.
Gatherings include (but not limited to):
- a gathering to undertake voluntary or not-for-profit sporting, recreational, social, or cultural activities
- a gathering to undertake community club activities
- a faith-based gathering
- a funeral
- a gathering held in a defined space or premises of a workplace (other than a vehicle in use as part of a public transport service) that have been hired for the exclusive use of the gathering by a person (other than the person who manages or controls the defined space or premises)
This excludes a gathering for the purpose of a business or service:
- at an office workplace
- as part of its ordinary retail operations
- at a hearing of a court or tribunal
- as part of its ordinary operations at an education entity
What defines an Event?
An Event is any activity organized by a business or service where entry is controlled (whether through ticketing, fees, registration, or any other means) that is held at:
- Any commercial premises or private premises (whether indoors or outdoors)
- Publicly-owned premises hired for the purpose of the activity
- An outdoor area where a group of customers and clients is accompanied or supervised by a worker providing services to that group (for example, a guided tour).
This includes normal operations at cinemas, theatres, stadiums, concert venues, conference venues, and private galleries; but excludes any activity at a private dwelling house.
Border control
Airports
For more information on international and domestic travel, please refer to the Cook Islands Travel page. View Travel Advisory HERE.
Outbound travel to New Zealand remains unaffected. Travel to the Pa Enua may have restrictions depending on their COVID-19 situation.
Seaports
The Cook Islands sea ports are now open with the normalisation of COVID-19.
COVID-19 Testing
There are three types of tests conducted in the Cook Islands to identify the SARS-CoV-2 virus, that causes COVID-19: 1) RT-PCR, 2) Serology and 3) RAT.
RT-PCR (real time polymerase chain reaction) tests are the gold standard for COVID-19 testing. Samples are collected in two ways: nasopharyngeal (via the nose) swabs or oropharyngeal (via the mouth) swabs. The PCR test detects genetic material from the virus, the RNA – if it is present, you may receive a positive test result indicating infection.
Serology tests are conducted using your blood sample. It detects antibodies in your body and checks your immune response toward COVID-19. A positive serology test result may indicate past infection. A serology test is not diagnostic, but useful for surveillance.
RAT (Rapid antigen test) is generally taken with a front nose swab and detects the presence of specific COVID-19 proteins, such as the nucleocapsid or spike protein. Results can show around 20 minutes after collecting the nose swab sample.
Laboratory testing for COVID-19 involves a mixture of in-country testing, and sending swabs to New Zealand reference laboratories for analysis. You can only receive a test if it is ordered by a clinician at Te Marae Ora. However, in an effort to prevent the spread of COVID-19, RAT kits are available for purchase at your local pharmacy or contact the Puna Clinics. Businesses that received RAT kits also have selected staff members that have been trained and are capable administering a RAT. If you are travelling to the Pa Enua (Outer Islands) or overseas and require a COVID-19 test, testing is available at the Rarotonga Airport.
Frequently Asked Questions
COVID-19 is a new respiratory illness. It is caused by a virus called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The virus was first reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, China. The World Health Organization declared it a pandemic on 12 March 2020.
Common symptoms include a new or worsening cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, cold-like symptoms (such as sneezing and runny nose), and a loss of smell, with or without fever (>38°C).
The SARS-CoV-2 virus, that causes COVID-19, is spread through the following modes: 1) large droplet spread; 2) aerosalised spread (for example coughing and sneezing); and 3) contact with respiratory secretions (for example contaminated surfaces).
You can become infected through direct contact with infected droplets released through coughing, sneezing, talking, singing or even hugging others. If infected droplets land on a surface or object, you can become infected by putting your hand on the contaminated surface/object and touching your face, mouth or nose.
- COVID-19 tests are available for free at community-based testing centres in Auckland.
- Please contact your usual GP in New Zealand for further information regarding testing centre. If you do not have an Auckland based GP, please contact Te Marae Ora on email: tmo.exemptions@cookislands.gov.ck
- When you present for your test, ensure you have a mobile number and email address so that the test results can be sent to your phone and/or forward the results to Te Marae Ora on email: tmo.exemptions@cookislands.gov.ck.
- If you require further assistance contact your GP. It will be the responsibility of the traveller to make the necessary arrangements and cover any associated cost with undertaking COVID-19 testing prior to departure
- As soon as possible, noting that results may not be available for one to three days.
- COVID-19 tests must be arranged within 96 hours of your flight departing Auckland.
- No.
- If you know you will not be receiving the results of your COVID-19 test prior to your check-in, please contact Te Marae Ora directly by either; email: tmo.exemptions@cookislands.gov.ck or Phone: Cook Islands +682 29 110
- You cannot travel directly to the Cook Islands from Australia (or any other country). You will be required to stay in New Zealand for 14 days.
- Please check the New Zealand Government Managed Isolation and Quarantine website for applicable charges to enter their managed isolation facilities. https://www.miq.govt.nz/
- Once Te Marae Ora has received the results of your COVID-19 test result (negative), your details will be communicated to Immigration Cook Islands who will provide final approval for you to travel to the Cook Islands.
Quarantine and isolation
The Difference between quarantine and isolation
Quarantine is required if you’ve been identified as a household or close contact of someone who’s tested positive for COVID-19. You will need to undergo tests, even if asymptomatic.
- For households contacts: 7 day quarantine period
- For close contacts: 7 day quarantine period
Facilities
Please note that accommodation facilities, including food & beverage requirements, are borne by the individual. We highly recommend you secure COVID-19 Travel Insurance.
What to expect
Should you be issued an isolation or quarantine order while in the Cook Islands, here is what you can expect.
Isolation/Quarantine
- Accommodation costs for the isolation period will be borne by the individual.
- Costs for food, beverages and other items will be borne by the individual.
- Any tests required as per the Isolation Order has no cost associated to it, as this is a requirement from Te Marae Ora
- Whilst in isolation, the Health Clinics will monitor you. This monitoring will be conducted via phone call only with exception that a face to face when required
- The Punas will support the Health Clinics with regards to delivery of items (if any) and the delivery of medications.
- An isolation pack will be given to you. This pack contains an information booklet and symptom diary to help you monitor and record your symptoms
- Upon receiving your isolation orders, you will also be given an isolation criteria and pamphlet from NZHC with useful numbers to contact. This is to help you be as self-sufficient as possible
Frequently Asked Questions
COVID-19 is a new respiratory illness. It is caused by a virus called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The virus was first reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, China. The World Health Organization declared it a pandemic on 12 March 2020.
Common symptoms include a new or worsening cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, cold-like symptoms (such as sneezing and runny nose), and a loss of smell, with or without fever (>38°C).
Less common symptoms include diarrhoea, a headache, nausea or vomiting, muscle pain or body aches, abdominal pain, chest pain, joint pain, confusion or irritability and malaise (a feeling of discomfort or unease).
The SARS-CoV-2 virus, that causes COVID-19, is spread through the following modes: 1) large droplet spread; 2) aerosalised spread (for example coughing and sneezing); and 3) contact with respiratory secretions (for example contaminated surfaces).
You can become infected through direct contact with infected droplets released through coughing, sneezing, talking, singing or even hugging others. If infected droplets land on a surface or object, you can become infected by putting your hand on the contaminated surface/object and touching your face, mouth or nose.
The spread of the virus by aerosols have increased the risk of transmission or contraction. Now the risk of airborne transmission is higher when in enclosed spaces with no airflow, crowded areas and close contact settings (this includes conversations, singing and shouting). The risk is lowered in outdoor settings, less people and if people are social distancing.
- COVID-19 tests are available for free at community-based testing centres in New Zealand. Click here to view testing stations.
- In Rarotonga, you can arrange a COVID-19 test at your own expense at Tupapa Primary Healthcare. Free testing is available at the local clinics/Punas. Click here to see the closest Clinic/Puna near you.
- COVID-19 tests are available strictly for travellers going to the Outer Islands/Pa Enua, at the Rarotonga International Airport testing station. A single RAT test cost $10 NZ dollars.
- Please contact your usual GP in New Zealand for further information regarding testing centre. If you do not have an Auckland based GP, please contact Te Marae Ora on email: tmo.exemptions@cookislands.gov.ck
- Ensure you have your mobile number and/or email address ready as this is how your COVID-19 test results will be sent to you. Please note that if you are travelling and need to present a negative COVID-19 test result, text messages may not be accepted. Click here to view travel criteria or visit our travel page.
- If you require further assistance contact your GP. It will be the responsibility of the traveller to make the necessary arrangements and cover any associated cost with undertaking COVID-19 testing prior to departure.
- If you are presenting cold, flu or COVID-19 like symptoms
- If you have been to any locations of interest or are a close contact of a positive COVID-19 patient
- If you have fallen under mandatory testing
- If you are travelling.
- You cannot travel directly to the Cook Islands from Australia (or any other country). You will be required to stay in New Zealand for 10 days.
- Please check the New Zealand Government COVID-19 website for more international travel information.
Isolation is highly encouraged if you return a positive COVID-19 test. Isolation period is 7 days.
